Anti-Tuberculosis Therapeutics Market (By Disease Type: Active TB, Latent TB & Others. By Diagnosis Type: Blood Tests, Sputum Tests, Imaging Tests & Others. By Dosage Type: Tablets and Capsules, Injections & Others. By Region - North America, Europe , Asia-Pacific , LAMEA) - Global Market Analysis, Growth, Trends & Forecast, 2022-2032
Report Type : Syndicate Report
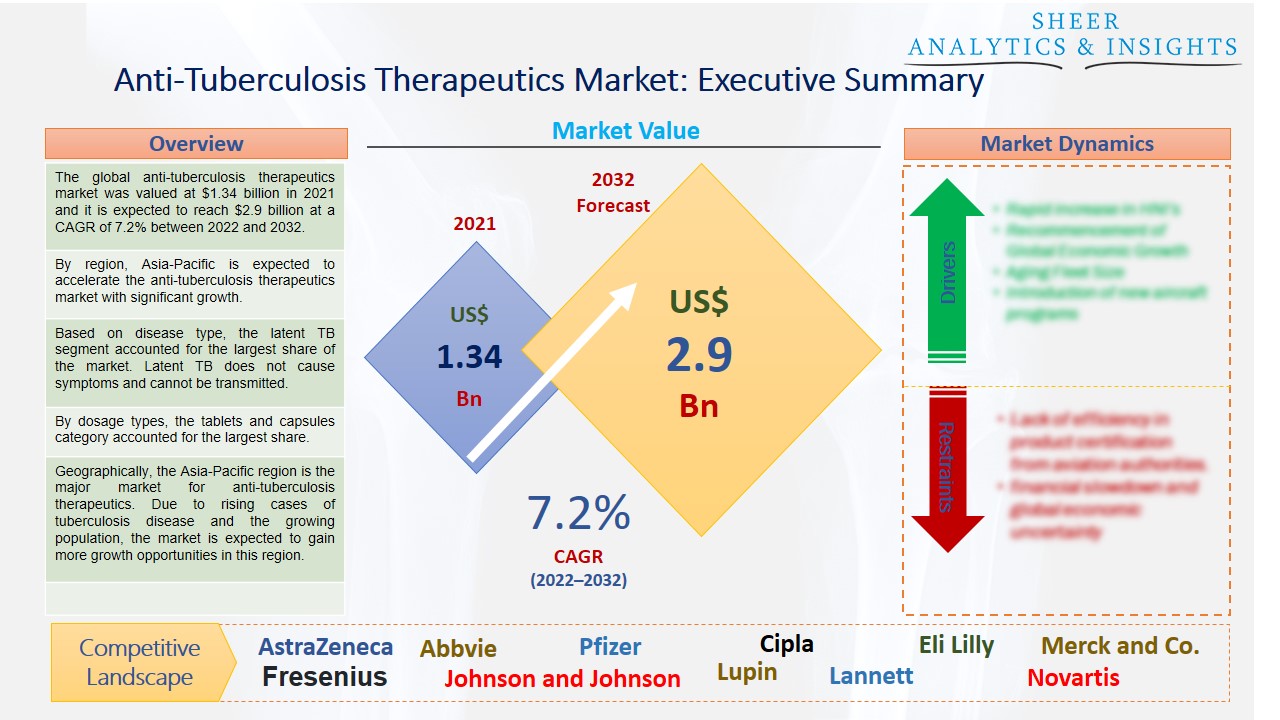
The global anti-tuberculosis therapeutics market was valued at $1.34 billion in 2021 and it is expected to reach $2.9 billion at a CAGR of 7.2% between 2022 and 2032. The market for anti-tuberculosis treatments is expanding at a rapid clip due in large part to the increased prevalence of tuberculosis. When they cough, sneeze or spit, people with lung TB release the TB germs into the air. By breathing in some of these bacteria, one becomes ill.
By region, Asia-Pacific is expected to accelerate the anti-tuberculosis therapeutics market with significant growth.
The FDA has approved the use of anti-tubercular drugs to treat infections caused by Mycobacterium TB, including rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. The term "ant-tubercular drugs" refers to a class of treatments used to treat tuberculosis. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M-TB), acid-fast aerobic bacteria that can grow on gram stain as either gram-positive or gram-negative, is the disease-causing agent of tuberculosis (TB). The benefits, risks, and other information on these medications will be covered in this review. The increasing healthcare spending, which helps to improve its infrastructure, is a crucial element influencing the growth rate of the anti-tuberculosis pharmaceuticals market. The market dynamics will be further impacted by various government organizations’ efforts to strengthen the healthcare infrastructure by boosting funding. An infectious disease called tuberculosis (TB) typically affects the lungs. The spine and brain are just two additional bodily regions where this disease can progress. It is brought on by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Pharmaceutical companies are focusing their efforts on developing drugs that can shorten the duration of therapy and assist in overcoming the challenges posed by drug-susceptible and drug-resistant tuberculosis. First-line treatment, second-line treatment, and drug-resistant treatment are the two types of tuberculosis treatment.
Source: SAI Research
Download Free PDF Sample Request
Curing the individual patient, lowering the danger of death and disability, and reducing the spread of M. tuberculosis to other people are the three main objectives of treatment for TB disease. TB disease must be treated for at least 6 months and in some cases even longer, to guarantee that these objectives are achieved. The market for anti-tuberculosis treatments is anticipated to develop faster than average due to the growing elderly population. Due to their weakened immune systems, older people are more vulnerable to both acute and chronic illnesses. Diabetes, HIV/AIDS, renal ailments, and other illnesses are among the main causes of immune system deterioration. Additionally, as certain medications, such as chemotherapy and those for the treatment of Crohn's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis, can impair immunity, they raise the chance of contracting tuberculosis. These primary factors are expected to drive the market and are anticipated to gain more growth opportunities for the market.
Due to the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act's ability to bring millions of presently uninsured Americans into the healthcare system, the existing efforts to combat tuberculosis (TB) in the US could be strengthened. To ensure that the right services are widely and easily accessible, the US government is also expected to support the collection, analysis, and use of quality-assured data and technologies, such as mobile devices and geographic information services. These services can help identify the best locations for new care and treatment sites as well as existing sites that need to be strengthened. On the other hand, the market's growth rate would be hampered by the high cost of MDR-TB and XDR-TB (extensively drug-resistant TB) medications.
Based on disease type, the latent TB segment accounted for the largest share of the market. Latent TB does not cause symptoms and cannot be transmitted. However, if they do not receive treatment, they could go on to acquire active TB disease, transmit the illness to others, and become very ill. If they receive medical care, those with active TB disease can be treated and cured. As a source of infection for contacts, active tuberculosis (TB) has a higher burden of TB bacilli than latent TB. Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is the condition in which Mycobacterium tuberculosis is present in humans but no clinical symptoms, radiological abnormality, or microbiological signs of the infection are present.
In terms of diagnosis, the blood test segment holds most of the market share and is anticipated to drive the market during the forecast period. Skin tests are still the most popular method of diagnosing tuberculosis, while blood tests are increasingly employed. On the inside of your forearm, a tiny quantity of tuberculin is injected just beneath the skin. Sputum test is also available in several emerging countries which would also accelerate the market growth. Sputum culture is one of the finest methods for TB diagnosis. A sputum culture is a test to identify microorganisms that can lead to an infection, such as TB bacteria. A chemical that encourages the development of bacteria is combined with a sample of sputum.
By dosage types, the tablets and capsules category accounted for the largest share. The three drugs combined—rifampin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide—are used to treat tuberculosis (TB) infection. It can be administered either alone or along with one or more other TB medications. Rifampin works to either stop or destroy the growth of bacteria and is a member of the antibiotic drug class.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is the major market for anti-tuberculosis therapeutics. Due to rising cases of tuberculosis disease and the growing population, the market is expected to gain more growth opportunities in this region. Moreover, in Asia - Pacific Region, tuberculosis (TB) is the most common infectious disease-related cause of mortality. Unfavorable health outcomes are disproportionately experienced by people living in poverty, particularly those with inadequate access to high-quality healthcare, unemployment, housing, and transportation. These elements can make TB disease more likely and create obstacles to treatment, either directly or indirectly.
According to the study, key players such as AstraZeneca (U.K), Abbvie (U.S), Cipla (India), Eli Lilly (U.S), Fresenius (Germany), Johnson and Johnson (U.S), Lupin (India), Lannett (U.S), Pfizer (U.S), Merck and Co. (U.S), Novartis (Switzerland), STI Pharma (U.S), Sanofi (France), Teva Pharmaceuticals (Israel), Viatris (U.S), among others are leading the global anti-tuberculosis therapeutics market.
Scope of the Report:
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2021 | US$ 1.34 Billion |
| Market Volume Projection by 2032 | US$ 2.9 Billion |
| Forecast Period 2022 to 2032 CAGR | 7.2% |
| Base Year: | 2021 |
| Historical Data | 2019, 2020 and 2021 |
| Forecast Period | 2022 to 2032 |
| Segments covered |
By Disease Type: Active TB, Latent TB & Others By Diagnosis Type: Blood Tests, Sputum Tests, Imaging Tests & Others By Dosage Type: Tablets and Capsules, Injections & Others |
| Geographies covered |
North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, LAMEA |
| Companies covered | AstraZeneca (U.K), Abbvie (U.S), Cipla (India), Eli Lilly (U.S), Fresenius (Germany), Johnson and Johnson (U.S), Lupin (India), Lannett (U.S), Pfizer (U.S), Merck and Co. (U.S), Novartis (Switzerland), STI Pharma (U.S), Sanofi (France), Teva Pharmaceuticals (Israel), Viatris (U.S) & Others |
The Global Anti-Tuberculosis Therapeutics Market Has Been Segmented Into:
The Global Anti-Tuberculosis Therapeutics Market – by Disease Type:
- Active TB
- Latent TB
- Others
The Global Anti-Tuberculosis Therapeutics Market – by Diagnosis Type:
- Blood Tests
- Sputum Tests
- Imaging Tests
- Others
The Global Anti-Tuberculosis Therapeutics Market – by Dosage Type:
- Tablets and Capsules
- Injections
- Others
The Global Anti-Tuberculosis Therapeutics Market – Region Type:
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- India
- China
- Japan
- Australia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- LAMEA
- Middle East
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Chile
- Others
- Africa
- South Africa
- Egypt
- Others
Buy Chapters or Sections
Customization options available to meet your custom research requirements :
- Request a part of this report
- Get geography specific report
- Request historical analysis
- Check out special discounted pricing

